What is an electronic signature?
Electronic signatures are fast overtaking paper signatures in our increasingly connected, mobile, and remote workplaces. But what exactly is an electronic signature? In this blog, we reveal some facts you might not know about e-signatures.
What are electronic signatures?
An electronic signature, also called an e-signature or eSignature, and sometimes referred to as a digital signature, is a legally recognized way to indicate a signer agrees to the contents of an electronic message or document. According to the US E-Sign Act, an electronic signature is, “an electronic sound, symbol, or process, attached to or logically associated with a contract or other record and executed or adopted by a person with the intent to sign the record.” Let’s explain what this legalese really means.
Today, eSignatures are everywhere, but when we say “eSignature,” most people probably imagine a picture of a signature placed above a line on an official-looking document:

This is the most literal example of an eSignature, but many people are surprised to find out that checking a box that says “I Agree” when signing up for a social media account or making an online purchase is also an “electronic signature” under the ESIGN act. While an electronic signature can take many different forms that may or may not look like your John Hancock, the key words in the ESIGN definition are process and intent.
The link between process and intent
Whether signing manually or digitally, for a signature to be legal, the signer must have demonstrated their intent to sign, or that they meant to agree and sign a digital record and didn’t do it by accident. The key to demonstrating intent to sign is the signing process. There must be a sufficient number or combination of steps—clicking an obvious link to a signing ceremony, using a mouse to draw a signature, and/or checking a box that clearly says “Accept”—to show intent. Theoretically, any process that demonstrates intent to sign could constitute an eSignature.
Our eSignature solution
Constellation1 eSign, our fully web-based, customizable, and secure eSignature solution, uses an ironclad process to establish intent to sign to ensure all signatures are legally binding and non-repudiable (signers can’t claim later that they never signed the document). In fact, our eSignature process is even more secure than traditional pen and paper, protecting you and your business.
The Constellation1 electronic signature process:
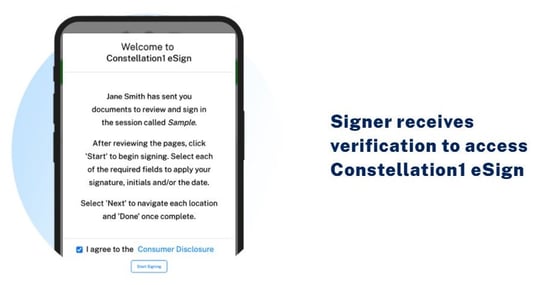 First, the signer receives a notification via email or text message to access their signing ceremony.
First, the signer receives a notification via email or text message to access their signing ceremony.

Next, the signer customizes their signature options, either by hand-drawing a signature or choosing a stylized signature for their name.
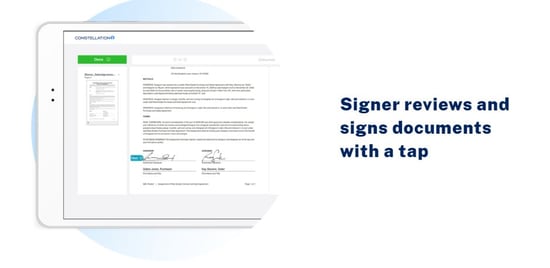
Next, the signer reviews the document and has to tap or click the screen to add their signature to the required fields. Documents may also contain check boxes and other fields.
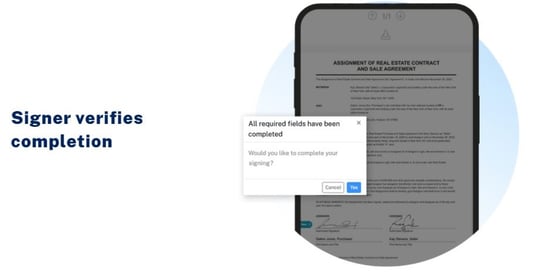
Lastly, before the signing ceremony is complete, the signer has to agree a final time to submit their signatures.
Constellation1 eSign’s other robust security features also ensure signers are who they say they are while keeping your important documents safe. Your team can use eSign with complete peace of mind.
For more information about Constellation1 eSign, download our free product brochure!
United States:
©2025 Constellation Web Solutions, Inc | All Rights Reserved | Privacy Policy | Terms | Do Not Sell My Information

